Everyone at Mead O'Brien would like to wish all of our customers,
vendors, suppliers, families and friends a very happy, healthy and
prosperous 2016!
We look forward to serving our customers and working alongside you for our mutual success and growth.
Cheers!
The Mead O'Brien Team
Providing problem solving and educational information for topics related to industrial steam, hot water systems, industrial valves, valve automation, HVAC, and process automation. Have a question? Give us a call at (800) 892-2769 | www.meadobrien.com
The Rotary Globe Control Valve
 |
| Neles Rotary Control Valve |
See the video below for a "look inside".
Valves Designed for Severe Service. Not Just Heavy Duty
 |
| High performance butterfly valve (Jamesbury) |
Severe service is a term that describes valves used in application at the extremes of pressure, temperature, cycling, and material compatibility. While there are plenty of published and accepted standards for industrial valves, one does not exist to precisely define a severe service valve.
So, what then defines the selection of severe service valves, as opposed to general purpose valves?
There are a number of basic selection criteria that might point you in that direction, but in general they are:
- Very extreme media or environmental temperature
- High pressure drop operation that may cause cavitation
- Rapid and extreme changes to inlet pressure
- Certain types or amounts of solids contained in the fluid
- Highly corrosive, or erosive process media.
Certainly, any of these criteria might be found in an application
serviceable by a general purpose valve, but their presence should be an
indicator that a more involved assessment of the fluid conditions and
commensurate valve requirements is needed. The key element for a
specifier is to recognize when conditions are apparent that
might exceed the capabilities of a general purpose valve, leading to
premature failure in control performance or catastrophic failure that
produces an unsafe condition. Once the possibility of a severe service
condition is identified, a careful analysis of the possible operating
conditions will reveal the performance requirements for the valve.
When in doubt, its critical to discuss your special requirements with an experienced product application specialist.
They have access to technical resources that can help with selecting
the right valve components to meet your severe service applications.
For more information contact:
(800) 892-2769
Closed Loop Control System Basics
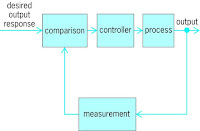 |
| Closed loop diagram |
A closed loop control system uses a sensor that feeds current system information back to a controller. That information is then compared to a reference point or desired state. Finally, a a corrective signal is sent to a control element that attempts to make the system achieve its desired state.
A very basic example of a temperature control loop includes a tank filled with product (the process variable), a thermocouple (the sensor), a thermostat (the controller), and a steam control valve feeding a tubing bundle (the final control element).
The video outlines all the major parts of the system, including the measured variable, the set point, the controlled variable, controller, error and disturbance.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
